The optical layer is realized through dedicated DWDM equipment which is able to provide up to
160 wavelengths per fiber link. The equipment currently provides 1 and 10 Gbit/s links 40
Gbit/s will be available soon. Through this (optical) link service a couple of LHCOPN links and a
lot of both national and international (through Geant2 or cbf) T2-T1 links (to GridKa) are
presently being provided. It is expected that especially for groups like the particle physicists this
way of networking will expand in the future.
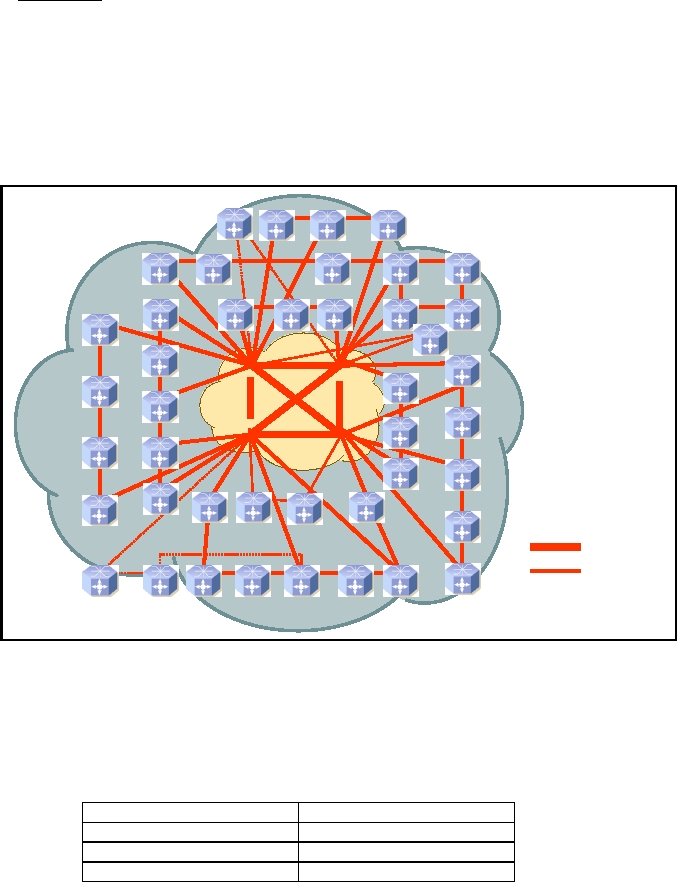
The IP layer is built on top of the optical layer. Figure 39 is showing the logical architecture of
the IP layer: A so called super core with CISCO's CRS-1-routers and the core with CISCO's
760x-routers built the basis for the IP layer.
7 6-
7 6-
7 6-
7 6-
Old 1
Ki e 1
Ros 1
Gr e 1
7 6-
7 6-
7 6-
7 6-
7 6-
Br e 1
De s 1
Tub 1
HUB 1
Ha m 1
7 6-
7 6-
7 6-
7 6-
7 6-
7 6-
Bi e 1
Ha n 1
Bra 1
Mag 1
ZIB 1
ADH 1
7 6-
7 6-
Go e 1
FFO 1
7 6-
CRS-
CRS-
7 6-
Mu e 1
Pot 1
Ha n 1
Dr e 1
7 6-
7 6-
Pot 1
Ka s 1
7 6-
Dui 1
7 6-
7 6-
CRS-
CRS-
Ch e 1
Ba y 1
Fra 1
Erl 1
7 6-
7 6-
Aa c 1
Mar 1
7 6-
7 6-
Erl 1
Lei 1
7 6-
7 6-
7 6-
7 6-
7 6-
7 6-
Bir 1
Fra 1
Wue 1
Reg 1
Aug 1
Gie 1
7 6-
Jen1
2x10GE
7 6-
1x10GE
7 6-
7 6-
7 6-
7 6-
7 6-
7 6-
7 6-
Il m 1
Saa 1
Kai 1
GSI 1
Hei 1
FZK 1
Stu1
Gar 1
Figure 39: Logical IP topology X-WiN (as of December 2007)
The DFNInternet service is provided by the core routers, which are placed in almost all DFN
PoPs (see Figure 38 ), to the routers of the research institutions or universities. With only a few
exceptions all these sites are connected to X-WiN. The following table reflects the access
capacities of the research institutions:
Access Bandwidth
# organisations
<100 Mbit/s
300
> 100 Mbit/s and < 10 Gbit/s
150
10 Gbit/s
4
Figure 40: Number and bandwidth of X-WiN accesses (DFNInternet)
75