Appendix 34. UltraScience Net: Network Research
Testbed for DOE Large-Scale Science Applications
Nagi Rao (raons@ornl.gov)
Bill Wing (wrw@ornl.gov)
UltraScience Net
Last updated January, 2007
The next generation of 100-1000 Teraflop supercomputers as well as national- and global-scale
grid systems needed for U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) large-scale science computations hold
an enormous promise for large-scale computational science projects from fields as diverse as
earth science, high energy and nuclear physics, astrophysics, fusion energy science, molecular
dynamics, nanoscale materials science, and genomics. These computations are expected to
generate hundreds of petabytes of data, which must be transferred, visualized and steered by
geographically distributed teams of scientists. In the experimental sciences area, DOE operates
several extremely valuable experimental facilities, for example, the Spallation Neutron Source.
The ability to remotely conduct experiments, and transfer large measurement data sets, can
significantly enhance the productivity of scientists and facilities. Indeed, the above networking
capabilities add a whole new dimension to the access of these computers and user facilities, by
eliminating the "single location, single time zone" bottlenecks. But, the existing testbeds and
networks for providing such channels typically have a very small footprint or bandwidth, offer
only a single lambda or sub-lambda, and are not field-hardened and optimized for wide-area
deployments.
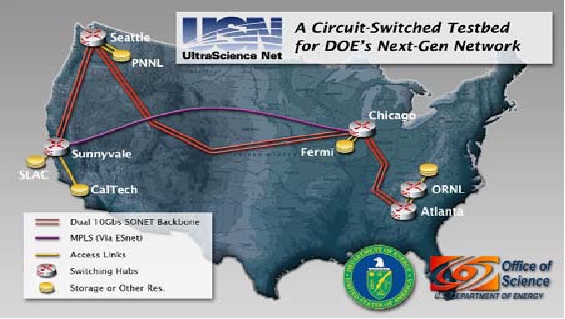
Figure 98: USN's dual 10bps links span Atlanta, Chicago, Seattle and Sunnyvale. It
connects ORNL, PNNL, FNL, SLAC, ESnet and Caltech.
UltraScienceNet (USN), shown in Figure 98, is an experimental network research testbed
dedicated to the development of networking capabilities needed for the above DOE large-scale
science applications. USN backbone consists of dual SONET OC192 10Gbps links that span
Atlanta, Chicago, Seattle and Sunnyvale as shown in Figure 99. It currently provides connectivity
to Fermi National Laboratory (FNAL), Oak Ridge National Laboratory (ORNL), Pacific
Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL), Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC), ESnet and
175