Inter-Domain Connectivity:
Data transfers in High Energy Physics typically have to cross multiple network domains. While
the above paragraphs have summarized how individual domains provide circuit-oriented services,
the end-to-end circuit provisioning has to address additional issues such as routing and
provisioning in a heterogeneous environment.
Control plane interaction between domains has been the subject discussed in working groups such
as the GLIF Control Plane Working Group 0. The main challenge stems from the fact that the
different domains might implement different data and control plane technologies. As proposed in
0, a unified Inter-Domain Communication mechanism based on Web Services technology can
provide the necessary functionality for inter-domain circuit provisioning, and a recent proposal
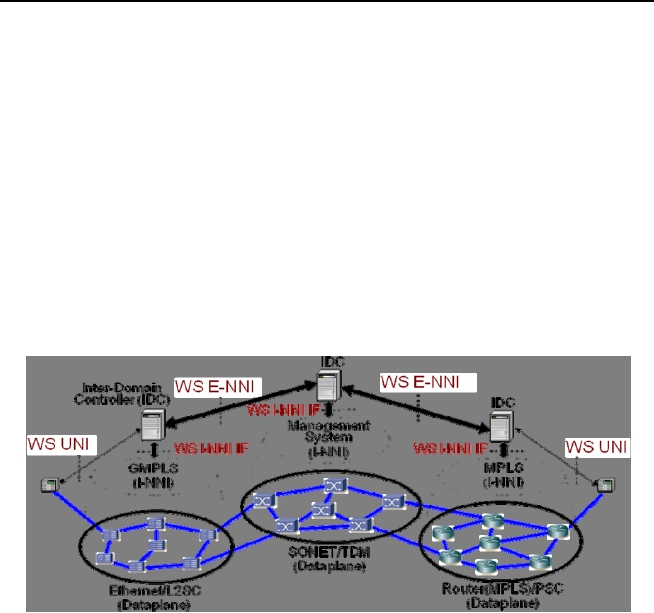
Visible in this picture is the use of different technologies used in autonomous domains, each
having its own implementation of the intra-domain control plane (e.g. (G) MPLS or NMS based),
as well as the inter-domain interaction between Inter-Domain Controller instances (IDC). The
interaction between the IDC and the intra-domain control plane is technology and domain
specific.
Figure 27 Control-Plane Interaction between domains for scheduling, routing and circuit
provisioning (T. Lehman et al., in 0).
The inter-domain control plane interface, called the External-Network-Network-Interface (E-
NNI), has three functions: topology exchange for routing, resource scheduling and signaling for
path provisioning, as shown in Figure 28. While the implementation of the IDC is left to the
domains, the protocol used between the domains is currently being standardized between
Internet2, ESnet, GEANT2, LambdaStation, TeraPaths and USLHCNet.
7
54